In this Blog, we will have insights about Apex Triggers and how to apply trigger concepts in real-time scenarios. This Blog is for the Beginners to Intermediate Level Developers. Read the blog till the end to know the BONUS TIP. Before wasting time let's get started.👍
The trigger is the piece of code that is executed when some specified database events occur.
Types Of Triggers:
1.Before Triggers: They are used to validate or update values of records before data is saved to the database.
2. After Triggers: They are used to access record values that are stored in the database and also when you have to make changes in other records.
Trigger Syntax:
Trigger <TriggerName> On <ObjectName> (trigger_events) {
//code
}
You may be wondering what is Trigger Events. So ,we have 7 Trigger Events in Salesforce apex triggers depending upon various DML operations:
- Before Insert
- Before Update
- Before Delete
- After Insert
- After Update
- After Delete
- After UnDelete
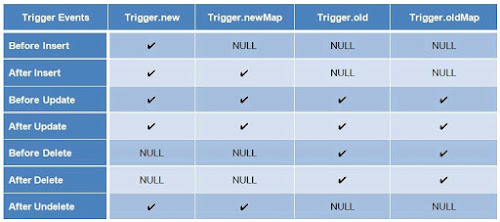
Context Variables: In order to access the records which are fired due to the Trigger, We use Context Variables in Trigger. For Example, the most commonly used Context Variables are Trigger.New and Trigger.Old.
Trigger.New contains all the new versions of records which have caused trigger to fire.Trigger.Old contains old versions of records.
You can check out all the Trigger Context Variables at the below link:
Check out the table to know which trigger events are allowed for 4 commonly used Trigger Context Variables.
Implementing the Trigger Scenarios:
Before diving directly into code, identify the below points from the given requirement scenario.
1.Object on which Trigger is fired.
2.Which Trigger Events should be used and Why?
3.Objects, fields, and conditions on which DML operations need to be performed.